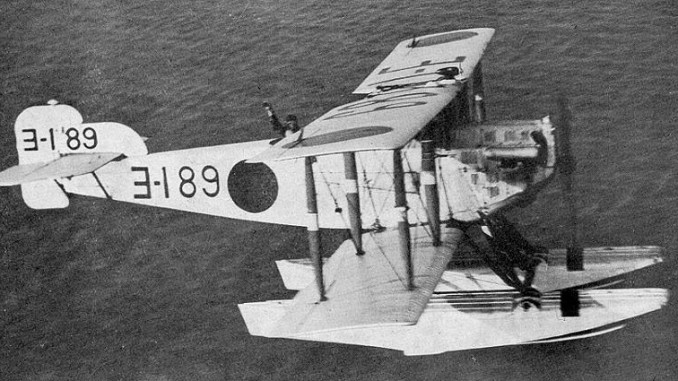
The Yokosuka E1Y was designed by a team from the Japanese Naval Arsenal in 1921, with the team being led by visiting members of Short Brothers, a UK aircraft manufacturer. Initial versions were very overweight and thus performed poorly, but later ‘Model B’ versions were substantially lighter and showed better stability and controllability. The Model B design was revised again to produce the final version in 1926, which resulted in the E1Y. The plane was given the designation Type 14 because it was accepted in to service in the 14th year of the Taisho Era.
The Type 14 was a biplane with fabric covered wings, seats for a pilot and an observer, and a license built Lorraine-Dietrich engine which produced 400hp. The observer was armed with a 7.7mm machine gun on a flexible mount, whilst 250kg of bombs could be carried.
Type 14s operated from battleships and cruisers as well as dedicated tender vessels. The aircraft operated from the seaplane tender Notoro during the ‘Shanghai Incident’, where it was used to bomb the city in what has been labelled as history’s first terror bombing.
Newer aircraft had almost entirely replaced the Type 14 in front-line service by the time the Sino-Japanese War began in 1937, and the type was relegated to training and other second-line activities, with some of the type being sold into civilian use.
Yokosuka E1Y Type 14 Specifications
| Yokosuka E1Y3 | |
| Role | Reconnaissance seaplane |
| Crew | 3 |
| Powerplant | 1x Lorraine-Dietrich 12E (450hp) |
| Speed | 81mph (cruise) 110mph (max) |
| Ceiling | 13,100ft |
| Range | 718 miles (internal) |
| Armament | 1x Type 89 7.7mm Machine gun |
| Ordnance | 240lb bombs |
| Dimensions | 34ft 9in (length) 46ft 8in (wingspan) 13ft 8in (height) |
| Wing Area | 584 sq.ft. |
| Weight | 4,164lb (empty) 6,062lb (gross) |
| Number produced | 102 |



Leave a Reply